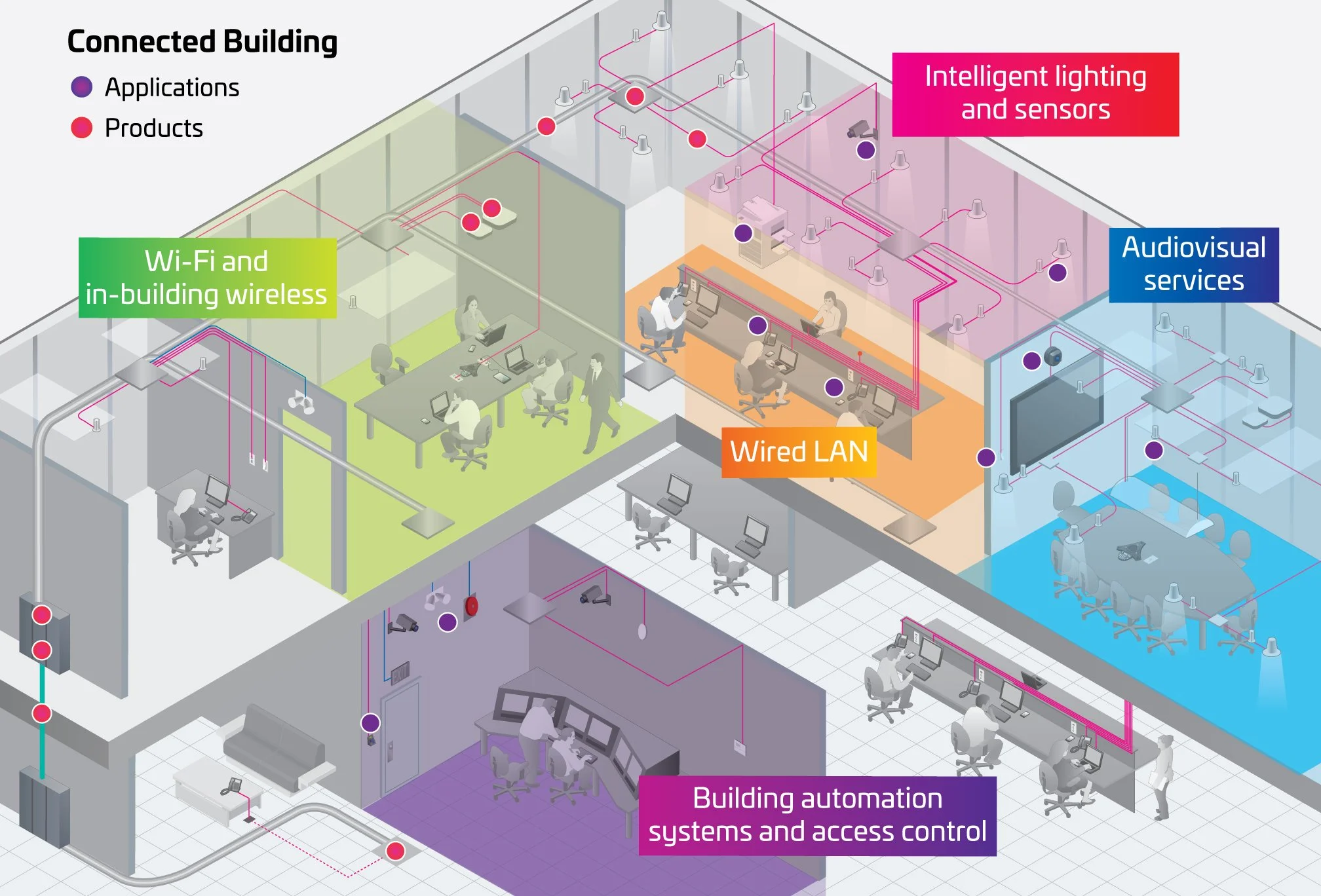
10 Factors to Consider Before Installing Network Cabling in Your New Facility
Installing network cabling in a new facility—whether it’s an office, warehouse, or data center—is one of the most important steps in building a high-performing and future-proof IT infrastructure. A well-designed cabling system can improve connectivity, reduce downtime, and make scaling your operations far easier down the road.
To help you avoid common pitfalls and get your infrastructure right the first time, we’ve compiled the ten most important things to consider before starting your network cabling installation.
1. Understand Your Facility's Layout
Before you start laying down cables, it's crucial to have a deep understanding of your facility's layout. The architecture of the building, including walls, floors, and ceilings, will directly influence how and where you can route your cables.
Building Architecture: Identify potential obstacles like load-bearing walls or restricted areas that could limit your cabling options. Understanding the structure will help you plan the most efficient cable pathways.
Cable Pathways: Think about the best routes for your cables. Overhead pathways might be ideal in a data center, while underfloor channels could be more suitable in an office environment. Properly planned pathways will reduce the risk of damage and ensure easy access for maintenance.
Accessibility: Ensure that your cabling is accessible for future upgrades or repairs. Installing cables in hard-to-reach places might save time initially but could lead to costly interventions down the line.
2. Define Network Requirements
Your network's performance depends on how well you define your requirements before the installation begins. Assessing both current and future needs is key to ensuring that your network can handle your operations efficiently.
Current and Future Needs: Analyze your current network demands and predict how these might grow. For example, if you plan to expand your workforce or adopt new technologies, your network should be able to scale accordingly.
Bandwidth and Speed: Different operations require different levels of bandwidth. High-definition video streaming, for instance, demands more bandwidth than simple data transfers. Ensure your cabling supports the necessary speed and bandwidth for your operations.
Network Segmentation: Consider segmenting your network to separate different types of traffic, such as data, voice, and security systems. This approach can enhance performance and make troubleshooting easier.
3. Choose the Right Cable Types
The type of cable you choose will have a significant impact on your network's performance and longevity. Making the right choice depends on understanding the advantages and limitations of each cable type.
Copper vs. Fiber Optics: Copper cables, such as Cat5e or Cat6, are cost-effective and suitable for shorter distances. However, if you need to cover long distances or require higher speeds, fiber optic cables are the better option, offering greater bandwidth and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Cable Categories: Different categories of cables (e.g., Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a) are designed for different performance levels. Cat6a, for example, supports higher data transfer speeds and longer distances compared to Cat5e.
Environmental Factors: Your facility’s environment will influence your cable choice. High temperatures, humidity, and potential interference from other electronic devices can degrade certain cable types. Choose cables that are rated for your specific environmental conditions.
4. Plan for Cable Management
Effective cable management is critical for maintaining a clean, organized, and easily maintainable network infrastructure. Without it, your cabling could quickly become a tangled mess, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased risk of damage.
Cable Organization: Use cable ties, Velcro straps, or cable trays to keep your cables organized. Proper organization not only looks professional but also makes it easier to identify and resolve issues.
Labeling: Labeling your cables is an essential step in cable management. Clearly marked cables allow for quick identification, which is crucial during troubleshooting or when changes need to be made.
Cable Trays and Conduits: Secure your cables using trays, conduits, or racks. These solutions help prevent damage, reduce clutter, and make it easier to add or remove cables in the future.
5. Compliance with Industry Standards
Adhering to industry standards and local regulations is not just about following rules; it’s about ensuring safety, reliability, and future-proofing your network.
Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Standards: CSA have established standards for telecommunications cabling. Adhering to these standards ensures your network is reliable and compatible with future upgrades.
Local Building Codes: Local building codes vary, but they typically cover aspects like fire safety and the structural integrity of installations. Make sure your cabling plan complies with all relevant regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure safety.
Fire Safety: Cabling through walls, ceilings, or floors may require specific fire-resistant materials or methods to comply with fire safety codes. Ensure your cabling plan addresses these requirements to protect your facility and its occupants.
6. Budgeting and Cost Considerations
While it might be tempting to cut costs, skimping on your cabling infrastructure can lead to greater expenses in the long run. It's important to plan a budget that allows for quality materials and professional installation.
Material Costs: Quality cables, connectors, and other materials may come with a higher price tag, but they offer better performance and longevity. Consider the long-term benefits of investing in high-quality materials.
Labor Costs: Professional installation is another area where cutting costs can be detrimental. Skilled technicians ensure that your cables are installed correctly, reducing the risk of future issues and saving money over time.
7. Plan for Integration with Existing Systems
If your new facility will connect with an existing network, it’s essential to ensure your cabling setup is compatible and scalable. Incompatibility between new infrastructure and current hardware can create headaches and performance issues down the road.
Compatibility: Confirm that the new cabling system supports your existing servers, switches, and routers. Using incompatible materials or outdated cabling can create bottlenecks or outright failures.
Scalability: Don’t just design for today. Whether you’re expanding your team, deploying cloud services, or integrating new technologies, your cabling infrastructure should be able to support future demands without requiring a full system overhaul.
Security: Physical cabling is often overlooked in cybersecurity planning. Choose secure pathways, install proper grounding, and ensure access points to cabling infrastructure are physically protected.
8. Consider Environmental Impact
Sustainability is becoming a major factor in infrastructure decisions. The cabling you choose—and how you dispose of or recycle existing cabling—can influence your environmental footprint.
Energy Efficiency: Use cabling systems that reduce power loss over distance and consider PoE (Power over Ethernet) to centralize and optimize power use for certain devices.
Sustainable Materials: Look for cabling products that use recycled or eco-friendly materials. This small step can contribute to larger environmental goals, especially in LEED-certified or green buildings.
Responsible Disposal: If you’re replacing old infrastructure, develop a plan to recycle cables and components. Many contain materials like copper that are both valuable and recyclable.
9. Hire Qualified Professionals
Your cabling infrastructure isn’t something you want to gamble with. Improper installation can result in degraded performance, costly downtime, and safety hazards.
Experience and Certification: Choose licensed installers with experience in commercial and industrial settings. Certifications such as BICSI or manufacturer-specific training (for fiber optics, for example) are a strong indicator of expertise.
Project Management: Look for a team that provides project oversight from start to finish. Coordinating with other trades (HVAC, electrical, flooring) ensures your cabling is installed efficiently and without delays.
Testing and Documentation: A quality job includes comprehensive testing—like signal integrity and loss—and full documentation of every pathway, outlet, and cable used.
10. Perform Thorough Testing and Validation
Once your cabling system is in place, your job isn’t quite finished. You need to ensure every component is working as expected and ready to handle real-world loads.
Performance Testing: Use network testers to check bandwidth, interference, and signal loss. These tools verify whether the cabling can support the data demands of your workplace.
Troubleshooting: Even with the most precise planning, issues can arise during or after installation. Be prepared with tools, techniques, and support staff to fix problems before your network goes live.
Documentation: Keep thorough records, including layout maps, cable IDs, and test results. This is invaluable for future upgrades, troubleshooting, or renovations.
Not sure which network cable is right for your setup?
Cabling may not be the most visible part of your infrastructure, but it’s one of the most important. With the right planning, components, and installation partner, your cabling project will deliver reliability, performance, and room for growth.
At Cabco, we’re here to help you make confident, informed decisions about your cabling infrastructure. Whether you’re starting from scratch or upgrading your current system, our team is ready to guide you through every step of the process.
👉 Need expert help on your cabling project? Contact us or explore more insights in the Cabco Learning Centre.